Procedures
Preparatory requirements
Before installing the software, Entrust recommends that you familiarize yourself with:
-
The Oracle database TDE documentation and setup process.
-
The Entrust Cryptographic Security Platform Key Management Vault Database Vault documentation.
-
Entrust recommends that you create a policy for managing SQL scripts that allow use of credentials for the Oracle database. These SQL scripts should only be available to authorized users.
This guide assumes that Oracle database software, and (at least) one Oracle database, is already installed on your system. With Oracle database software already installed, ensure that any required patches have been added. Oracle Data Guard is setup and working with a minimum of one standby server in place.
To integrate an Oracle database with Entrust Cryptographic Security Platform Key Management Vault Database Vault and Oracle Data Guard, the following steps are required:
-
Configure the environment.
-
Install the Entrust Cryptographic Security Platform Key Management Vault Database Vault software.
-
Configure Oracle database software to use the Entrust Cryptographic Security Platform Key Management Vault Database Vault.
-
Modify Oracle Data Guard configuration so encrypted data on primary server is also migrated and visible on the standby servers.
Details of your installation and configuration will depend on whether you want to migrate encryption keys from an existing Oracle software keystore to Entrust Cryptographic Security Platform Key Management Vault, or start directly with Entrust Cryptographic Security Platform Key Management Vault.
The default host server user is oracle unless stated otherwise.
The example database used in this guide is CDB1 unless stated otherwise.
For more information on how to configure your Entrust environment, see the Key Management Vault Installation and Upgrade Guide.
For more information on how to configure your Oracle environment, see the Oracle documentation.
Oracle Data Guard Environment
For the purpose of this integration procedure, we will use a primary and standby server for Oracle Data Guard. For reference the following table has been created so the user can visualize the environment:
| Site | Primary | Standby |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Create a Database Vault in the Key Management Vault Server
The Key Management Vault appliance supports different type of vaults that can be used by all type of applications. This section describes how to create a Database Vault in the Key Management Vault Server. See Creating a Vault for more details.
-
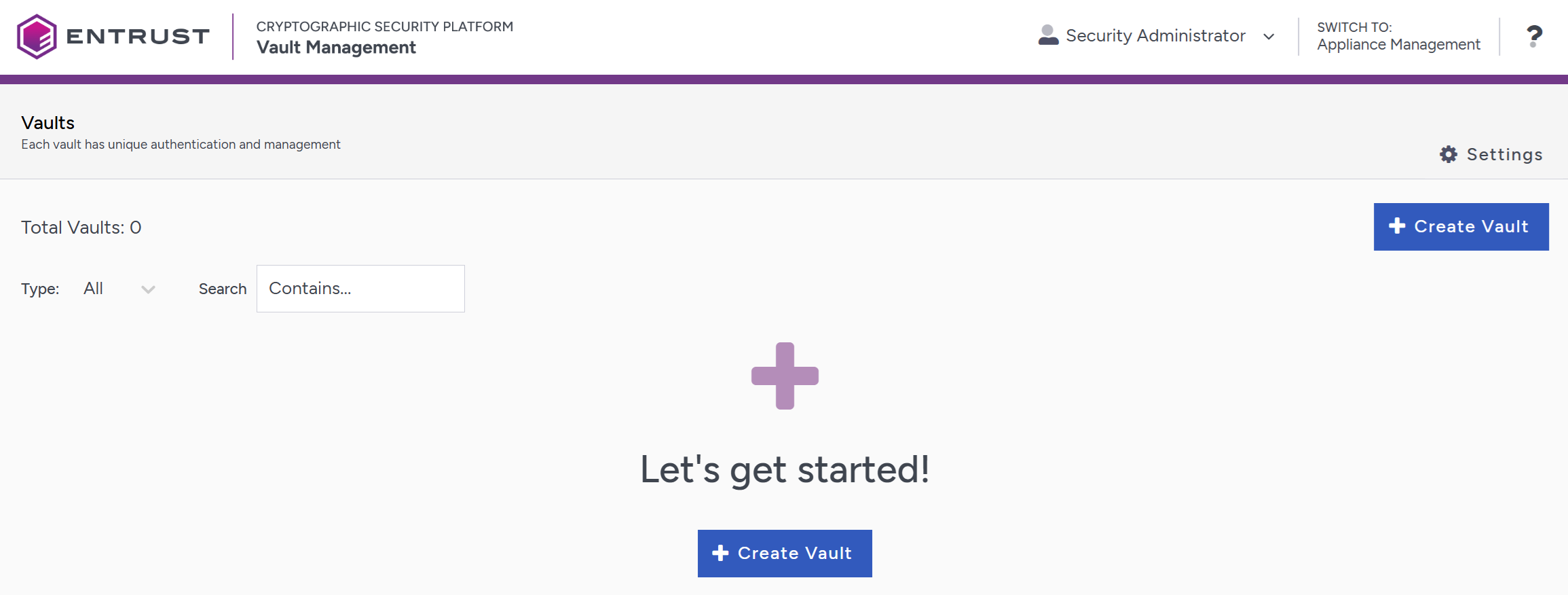
Log in to the Key Management Vault server in your web browser using the secroot credentials to access the IP address of the server.
-
If you are not in the vault Management interface, select SWITCH TO: Manage Vaults in the Menu Header
-
Select Create Vault.
-
Create a Database Vault:
-
For Type, select Database.
-
For Name, enter the name of the vault.
-
For Description, enter the description of the vault.
-
For Admin Name, enter the name of the administrator of the vault.
-
For Admin Email, enter a valid email for the administrator.
A temporary password will be emailed to the administrator’s email address. This is the password that will be used to sign in for the first time to the Database Vault space in the Key Management Vault. In a closed gap environment where email is not available, the password for the user is displayed when you first create the vault. That can be copied and sent to the user.
-
-
Select Create Vault.
-
Select Close when the vault creation completes.
-
The newly vault is added to the vault dashboard.
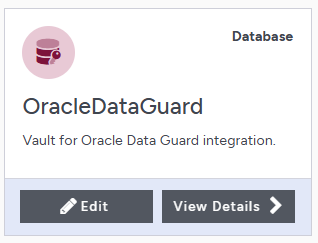
Sign in to the Database Vault URL
-
Sign in to the Database Vault URL provided when it was created with the temporary password that was copied.
-
Change the initial password when prompted.
-
Sign in again to verify.
Create a Node Mapping
A Key Management Vault node mapping helps Entrust clients on the database server nodes to failover in case one of the Key Management Vault node fails.
In the Cryptographic Security Platform Key Management Vault Database Vault webGUI:
-
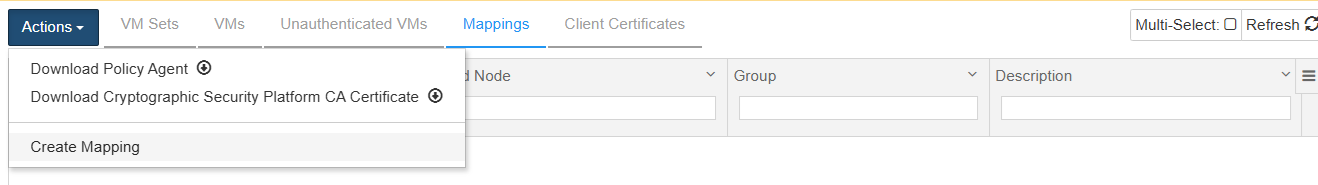
Navigate to Workloads
-
Select the Mappings tab.
-
In the Actions menu choose Create Mapping to create a new mapping.
-
In the Create New Mapping Dialog, in the Mapping tab, enter the following:
-
Name: Name of the mapping.
-
Cloud Admin Group: Select Cloud Admin Group (default).
-
Description: Description of the mapping.
-
Select Next.

-
-
In the Create New Mapping Dialog, in the Servers tab, enter the following for each Node in the Key Management Vault cluster:
-
External IP: IP address of the node.
-
Port: Enter 443.
-
CSP Server: Select the Key Management Vault Server.
-
State: Select Enabled.
-
Description: Description of the node.
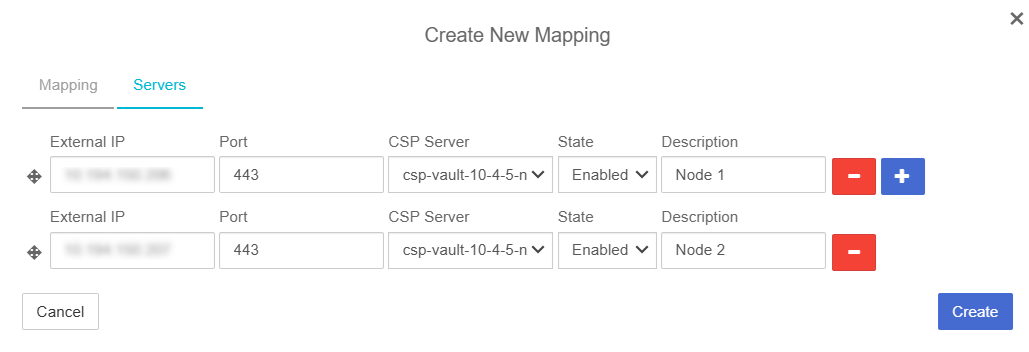
-
-
Select Create.
Once created the mapping gets listed.
Download TDE script bundle
In the Cryptographic Security Platform Key Management Vault Database Vault webGUI:
-
Navigate to Workloads.
-
Select the VM Sets tab.
-
In the Actions menu select Download TDE script bundle.
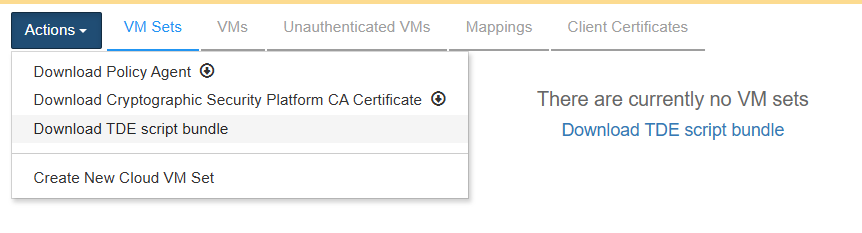
-
In the Download TDE Scripts bundle Dialog, enter the following:
-
Name: Provide a Name which will become prefix for your Keyset and CVMset. For example, if you choose oracle as Name then the setup script will create oracle_keyset and oracle_cvmset respectively.
-
Database Type: Select Oracle Database Server.
-
Enable HSM: If have an HSM configured and want to protect your TDE master keys with it, then choose Enable HSM. You will be required to verify the HSM connection to proceed, if you enable HSM.
-
CSP Nodes Mapping: In the drop down choose the CSP Nodes Mapping, if you have created one, or proceed without one.
-
Select Continue.
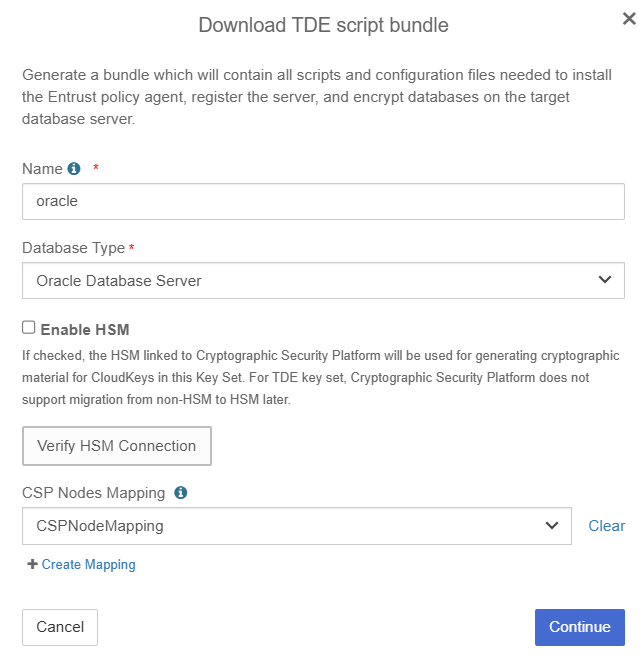
-
-
The TDE Scripts Bundle Details appear. Validate the information is correct and Select Download.
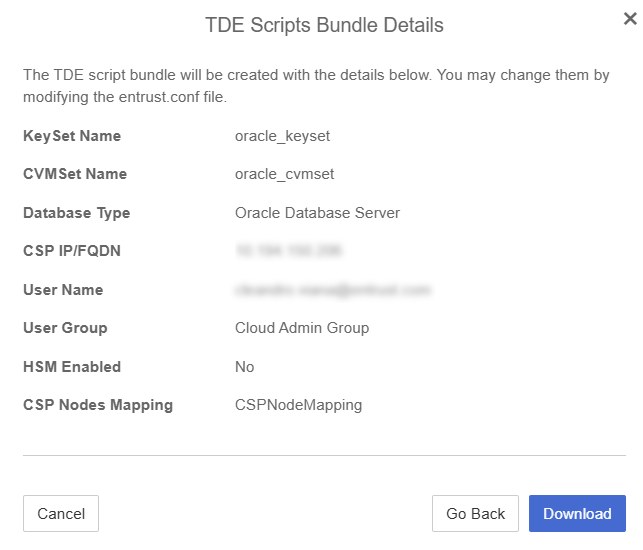
A zip file named with the name given in the Download TDE Scripts bundle dialog is downloaded, that is,
oracle.zip. Save this file as this will be used in each Oracle database instance server.
Entrust Cryptographic Security Platform Key Management Vault client setup on first Oracle database server node (primary)
-
Log in to the primary Oracle server as the
oracleuser. -
Create a directory for the bundle in the oracle’s user home directory.
% mkdir ~/csp -
Copy the TDE bundle downloaded earlier to the Primary Oracle server node.
The bundle is a zip file <name>.zip with <name> as provided by the admin while downloading the bundle. For this guide the name used was
oracle, so the name of the file isoracle.zip.% scp oracle.zip oracle@xx.xxx.xxx.xxx:/home/oracle/csp/. -
Extract the files in the bundle:
-
entrust.conf -
setup.sh
% cd ~/csp; unzip oracle.zip Archive: oracle.zip inflating: setup.sh inflating: entrust.conf -
-
Modify
entrust.conffile to match the environment.entrust.confis a config file which has most of the parameters pre-filled. You can still modify these values if you think that is required. There are some parameters which are specific to the Oracle database server and they need to be modified. Here is a list of the parameters which need to be set by the DB administrator:- oracle_user
-
this is the name of the database admin user, typically the value is
oracle - oracle_user_group
-
The group to which oracle_user belongs, typically the value is
oinstall.
Here is the
entrust.conffor our environment:+
# # kind of a cluster or setup name for your oracle RAC # it should be unique in a vault # Make sure these same parameters are used from all the nodes in your RAC cluster and DR nodes # dbset_name="oracle" # # KeyControl parameters # --------------------- # kcv_ip_or_fqdn="xx.xxx.xxx.xxx" # # If KeyControl mapping has been setup on the KC cluster, it can be provided here # kc_mapping="CSPNodeMapping" # # If KeyControl is configured with HSM then it can be enabled using "yes" as value # if not specified here then the default value is yes if KC has hsm enabled # enable_hsm="no" # # Vault parameters # --------------------- vaultid="4b551f9d-0442-45e1-ad6e-6a45ec2ce0af" user_name="xxxx.xxxx@entrust.com" # # Uncomment the password parameter, if you want to set it here # if you do not provide password for vault admin then setup script will prompt you # # password="password23!" # user_group="Cloud Admin Group" # # Oracle user parameters # ---------------------- # oracle_user="oracle" oracle_user_group="oinstall" # # hostname suffix is used only in qa testing, please do not uncomment it # hostname_suffix="dr" -
After editing entrust.conf, save the changes.
Set up the Client
Run setup.sh as the root user or using sudo.
We are doing this on the primary server, so we will use first as the first argument.
When we use this option, the keyset/vmset are created.
The script asks for the Key Management Vault Database vault administrator password and it prints the name of the access token file:
Saving access token in file `/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf`.Make a note of this as it will be used in the subsequent SQL statements to open the wallet.
% sudo ./setup.sh first entrust.conf
First node configuration in Oracle RAC
Enter password for xxxxx.xxxx@entrust.com:
Downloading hicli API from xxx.xxx.xxx.xx6
Successfully downloaded and extracted Entrust KeyControl API
.
.
.
Successfully created access token
Saving access token in file /opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf
Set permission of access token so that user "oracle" can access it
Successfully set permissions
Create link to Entrust pkcs11 library in /opt/oracle/extapi/64/hsm/entrust
Successfully linked pkcs11 library
Setup completeIf the HSM is enabled in the settings of the Key Management Vault appliance manager and in the entrust.conf file enable_hsm is set to no, you may get a message like this when you run the setup.sh script:
Create keyset oracle_keyset
Server returned error: Failed to create Keyset root key
Failed to download policy agentIf that’s the case, please request a new version of the setup.sh script from Entrust support as this is a bug found during testing.
You can also just disable the HSM settings in the Key Management Vault and that will resolve the issue.
If you selected to use the HSM (enable_hsm set to yes), then the HSM settings in the Key Management Vault must be enabled.
Entrust Cryptographic Security Platform Key Management Vault client setup on second Oracle database server node (standby)
-
Login to the standby server as the
oracleuser. -
Create a directory for the bundle in the oracle’s user home directory.
% mkdir ~/csp -
Copy the TDE bundle downloaded earlier to the standby Oracle server node.
% scp oracle.zip oracle@xx.xxx.xxx.xxx:/home/oracle/csp/. -
Extract the files in the bundle:
-
entrust.conf
-
setup.sh
% cd ~/csp; unzip oracle.zip Archive: oracle.zip inflating: setup.sh inflating: entrust.conf
-
-
Copy the modified entrust.conf from the first (primary) Oracle server node and overwrite the config file from the bundle.
% scp oracle@xx.xxx.xxx.xxx:/home/oracle/csp/entrust.conf . -
Run
setup.shas therootuser or usingsudo.sudo ./setup.sh other entrust.confNote that the value of first argument is
other.Second node configuration in Oracle RAC Enter password for xxxxxx.xxxxx@entrust.com: Downloading hicli API from xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx Successfully downloaded and extracted Entrust KeyControl API . . . Create Access Token Successfully created access token Saving access token in file /opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf Set permission of access token so that user "oracle" can access it Successfully set permissions Create link to Entrust pkcs11 library in /opt/oracle/extapi/64/hsm/entrust Successfully linked pkcs11 library Setup complete
Enabling TDE on non-encrypted Oracle Database
This section describes how to enable TDE if the database is not previously encrypted. If your database is already encrypted using software wallet then go to section Prerequisite for Migrating from software wallet to Key Management Vault.
The setup used in this section has a primary and a standby server. No RAC is used.
The following instructions assume the name of the database is CDB1. Please replace it with the name of database in your setup. CONTAINER=ALL is required for multitenant database, please remove it for non-multitenant database.
We will do this on the primary server.
First we must connect to the database as sysdba.
% sqlplus / as sysdbaShutdown the database
SQL> shutdown immediate;
Database closed.
Database dismounted.
ORACLE instance shut down.Set WALLET ROOT
Set the Oracle wallet location. Even though HSM Wallet does not reside on a local disk, this step is required to set TDE.
-
If the wallet directory doesn’t exist yet, create it as the
oracleuser.% mkdir -p $ORACLE_BASE/admin/$ORACLE_SID/wallet/tde -
Set
WALLET_ROOT:SQL> startup; ORACLE instance started. Total System Global Area 2147481656 bytes Fixed Size 8898616 bytes Variable Size 486539264 bytes Database Buffers 1644167168 bytes Redo Buffers 7876608 bytes Database mounted. Database opened. SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET WALLET_ROOT="$ORACLE_BASE/admin/$ORACLE_SID/wallet" scope=spfile; System altered. SQL> shutdown immediate; SQL> startup;
Set Hardware Keystore Type
Set the wallet type to HSM.
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET TDE_CONFIGURATION="KEYSTORE_CONFIGURATION=HSM" scope=both;
System altered.
SQL> shutdown immediate;
SQL> startup;Show wallet and keystore parameters
-
Show
wallet_root:SQL> show parameter wallet_root NAME TYPE VALUE ------------------------------------ ----------- ------------------------------ wallet_root string /opt/oracle/admin/CDB1/wallet -
Show
tde_configurationSQL> show parameter tde_configuration NAME TYPE VALUE ------------------------------------ ----------- ------------------------------ tde_configuration string KEYSTORE_CONFIGURATION=HSM
Open HSM keystore backed by Key Management Vault
-
Open the HSM keystore
Note here that we will point to the token file that was created when we setup the Entrust Key Management Vault client on the primary.
-- Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" CONTAINER = ALL; keystore altered. -- Non-Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf"; keystore altered. -
Show keystore state
SQL> select CON_ID,WRL_TYPE,STATUS from V$ENCRYPTION_WALLET; -- Multitenant output CON_ID WRL_TYPE STATUS ---------- -------------------- ------------------------------ 1 HSM OPEN_NO_MASTER_KEY 2 HSM OPEN_NO_MASTER_KEY 3 HSM CLOSED 4 HSM CLOSED -- Non-Multitenant output CON_ID WRL_TYPE STATUS ---------- -------------------- ------------------------------ 0 HSM OPEN_NO_MASTER_KEY
Generate the master encryption key
Create a TDE master encryption key that is stored inside the Entrust Key Management Vault. Oracle Database uses the TDE master encryption key to encrypt or decrypt TDE table keys and tablespace keys.
-
Create the TDE master encryption key.
This command performs two actions:
-
Create key in the Entrust Key Management Vault.
-
Use the created key in Oracle as master encryption key.
-- Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEY IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" CONTAINER = ALL; keystore altered. -- Non-Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEY IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf"; keystore altered.
-
-
Show keystore state
SQL> select CON_ID,WRL_TYPE,STATUS from V$ENCRYPTION_WALLET; -- Multitenant output CON_ID WRL_TYPE STATUS ---------- -------------------- ------------------------------ 1 HSM OPEN 2 HSM OPEN 3 HSM CLOSED 4 HSM CLOSED -- Non-Multitenant output CON_ID WRL_TYPE STATUS ---------- -------------------- ------------------------------ 0 HSM OPEN -
Bounce the database
SQL> shutdown immediate; SQL> startup;
Open HSM keystore, again
Every time the database is restarted, you have to open the HSM keystore, unless you setup Auto Login as described in Configuring Auto-login for the Key Management Vault Keystore.
-
Open the HSM keystore.
-- Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" CONTAINER = ALL; keystore altered. -- Non-Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf"; keystore altered.
Show encryption keys
-
Show the encryption keys.
SQL> select key_id,tag,keystore_type,creation_time from v$encryption_keys; KEY_ID TAG KEYSTORE_TYPE CREATION_TIME ---------------------------------- ----- ----------------- ------------------------------------ 064DCFB50BE6184F14BF5616A2C3A812D9 HSM 05-AUG-25 08.09.00.651573 PM +00:00
Identify KeyID in use
-
Identify the Key.
SQL> SELECT KEY_ID FROM V$ENCRYPTION_KEYS WHERE ACTIVATION_TIME = (SELECT MAX(ACTIVATION_TIME) FROM V$ENCRYPTION_KEYS WHERE ACTIVATING_DBID = (SELECT DBID FROM V$DATABASE)); KEY_ID ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 064DCFB50BE6184F14BF5616A2C3A812D9
Database Encryption with TDE keys
There are two types of encryptions considered in the guide: column level encryption and tablespace level encryption.
Column encryption
Since Columns are SYS owned objects, you will run into this error when attempting to encrypt a column in a database:
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-28336: cannot encrypt SYS owned objectsTo get around the problem you need to create a user and grant the necessary permissions. You will use this user to create the table and encrypt the column.
-
Create the User
SQL> CREATE USER C##test_user IDENTIFIED BY test_password; User created. -
Grant necessary privileges
SQL> GRANT CREATE SESSION, CREATE TABLE TO C##test_user; Grant succeeded. SQL> ALTER USER C##test_user QUOTA UNLIMITED ON USERS; User altered. SQL> ALTER USER C##test_user QUOTA 100M ON USERS; User altered. SQL> SELECT tablespace_name, bytes, max_bytes FROM dba_ts_quotas WHERE username = 'C##TEST_USER'; TABLESPACE_NAME BYTES MAX_BYTES ------------------------------ ---------- ---------- USERS 0 104857600 -
Connect as the new user.
SQL> CONNECT C##test_user/test_password; Connected. -
Create a table
SQL> CREATE TABLE CUSTOMERS (ID NUMBER(5), NAME VARCHAR(42), CREDIT_LIMIT NUMBER(10)); Table created. -
Add data to the table.
SQL> INSERT INTO CUSTOMERS VALUES (001, 'Rakesh Sharma', 10000); 1 row created. SQL> INSERT INTO CUSTOMERS VALUES (002, 'Betty John', 20000); 1 row created. SQL> INSERT INTO CUSTOMERS VALUES (003, 'T Ramchandran', 30000); 1 row created. SQL> INSERT INTO CUSTOMERS VALUES (004, 'Amir Khan', 40000); 1 row created. SQL> COMMIT; Commit complete. -
Encrypt a column.
SQL> ALTER TABLE CUSTOMERS MODIFY (CREDIT_LIMIT ENCRYPT); Table altered. -
List encrypted columns.
To do this you must connect as the sysdba user;
SQL> CONNECT sys/oracle as sysdba; SQL> SELECT * FROM DBA_ENCRYPTED_COLUMNS; OWNER TABLE_NAME COLUMN_NAME ENCRYPTION_ALG SAL INTEGRITY_AL --------- ----------- ------------- ----------------- --- ----------------------- TEST_USER CUSTOMERS CREDIT_LIMIT AES 192 bits key YES SHA-1
Verification
-
Connect as the test_user
SQL> CONNECT C##test_user/test_password; Connected. -
Get the encrypted data back.
SQL> SELECT CREDIT_LIMIT FROM CUSTOMERS; CREDIT_LIMIT ------------ 10000 20000 30000 40000 -
Close the wallet
To do this you must connect as the sysdba user;
SQL> CONNECT sys/oracle as sysdba; -- Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE CLOSE IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" CONTAINER = ALL; keystore altered. -- Non-Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE CLOSE IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf"; keystore altered. -
Connect as the test_user
SQL> CONNECT C##test_user/test_password; Connected. -
Now data retrieval should fail.
SQL> SELECT CREDIT_LIMIT FROM CUSTOMERS; ERROR at line 1: ORA-28365: wallet is not open -
Works again after opening the key store.
To do this you must connect as the sysdba user;
SQL> CONNECT sys/oracle as sysdba; -- Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" CONTAINER = ALL; keystore altered. -- Non-Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf"; keystore altered. -
Now the retrieval of the data should work.
You must connect as the test_user first.
SQL> CONNECT C##test_user/test_password; Connected. SQL> SELECT CREDIT_LIMIT FROM CUSTOMERS; CREDIT_LIMIT ------------ 10000 20000 30000 40000
Tablespace encryption
Data encryption keys are managed by Oracle. They are created as tablespaces are encrypted. The DEKs are wrapped with the master key and the wrapped keys are stored with the data. Oracle communicates with Key Management Vault to wrap / unwrap these data keys.
Make sure you are connected as sysdba.
-
Create encrypted tablespace, for example using AES256 algorithm
SQL> CREATE TABLESPACE SECURESPACE DATAFILE '/opt/oracle/oradata/CDB1/SECURE01.DBF' SIZE 150M ENCRYPTION using 'AES256' DEFAULT STORAGE (ENCRYPT); Tablespace created. -
Create a table in encrypted tablespace.
SQL> CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE (ID NUMBER(5),NAME VARCHAR(42),SALARY NUMBER(10)) TABLESPACE SECURESPACE; Table created. -
Insert data in the table.
SQL> INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (001,'JOHN LENON',100000); 1 row created. SQL> INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (002,'MARTINA HINGIS',200000); 1 row created. SQL> INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (003,'R ATTENBOROUGH',350000); 1 row created. SQL> COMMIT; Commit complete. -
Display the data.
SQL> SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE; ID NAME SALARY ---------- ------------------------------------------ ---------- 1 JOHN LENON 100000 2 MARTINA HINGIS 200000 3 R ATTENBOROUGH 350000 -
Display tablespaces.
SQL> SELECT t.name AS tablespace_name, e.encryptionalg AS encryption_algorithm FROM v$tablespace t JOIN v$encrypted_tablespaces e ON t.ts# = e.ts#; TABLESPACE_NAME ENCRYPT ------------------------------ ------- SECURESPACE AES256
Verification
-
Get the encrypted data back
SQL> SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE; ID NAME SALARY ---------- ------------------------------------------ ---------- 1 JOHN LENON 100000 2 MARTINA HINGIS 200000 3 R ATTENBOROUGH 350000 -
Close the HSM wallet.
-- Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE CLOSE IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" CONTAINER = ALL; keystore altered. -- Non-Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE CLOSE IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf"; keystore altered. -
Now data retrieval should fail.
SQL> SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE; ERROR at line 1: ORA-28365: wallet is not open -
Open the keystore.
Data retrieval works again after opening the keystore.
-- Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" CONTAINER = ALL; keystore altered. -- Non-Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf"; keystore altered. -
Retrieve the data - It should work!
SQL> SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE; ID NAME SALARY ---------- ------------------------------------------ ---------- 1 JOHN LENON 100000 2 MARTINA HINGIS 200000 3 R ATTENBOROUGH 350000
Oracle TDE Keys in the Key Management Vault WebGUI
The Oracle TDE keys are created by Oracle using the pkcs11 API directly. However, Key Management Vault shows these keys in the WebGUI. There are a limited set of operations that can be performed from the WebGUI.
In the Entrust Cryptographic Security Platform Key Management Vault Database Vault webGUI:
-
Navigate to Cloudkeys.
-
Select the CloudKeys tab.
-
For the Key Set, select the TDE keyset created by the TDE setup scripts.
-
The Keys that have been created by our encryption process in the previous section should be listed.
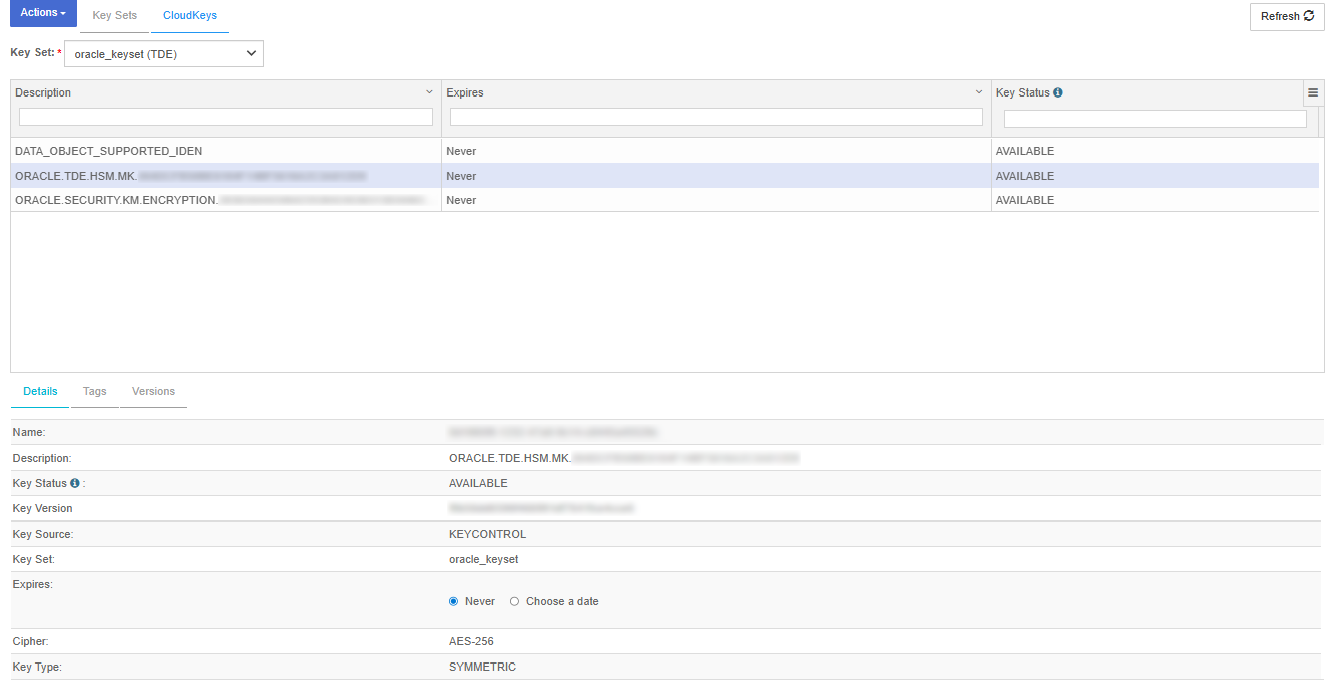
The keys starting with description:
-
ORACLE.TDE.HSM.MK : are the TDE master keys created by Oracle. These are used to encrypt TDE data encryption keys.
-
ORACLE.SECURITY.KM.ENCRYPTION : are generic keys managed by Oracle for TDE. They can be used to encrypt data or other keys.
-
DATA_OBJECT_SUPPORTED_IDEN : these are objects used by Oracle for access control purposes
-
Prerequisite for Migrating from software wallet to Key Management Vault
During migration from Software Wallet to the Key Management Vault Keystore, you may experience issues due to auto-login wallet set with the software keystore. To resolve this, disable the auto-login keystore to close all keystores.
Connect to the database as sysdba.
-
Shutdown the database.
SQL> shutdown immediate; -
Move the wallet file to a backup file.
% mv <path-to-keystorefolder>/<keystore-folder>/tde/cwallet.sso <path-tokeystorefolder>/<keystore-folder>/tde/cwallet.sso.backup -
Start the database
SQL> starup;
Migrating from software wallet to Key Management Vault
Connect to the database as sysdba.
% sqlplus / as sysdbaMultitenant
The following procedure applies when the target database is multitenant, and you are already using a software wallet with TDE encryption.
It is assumed the WALLET_ROOT parameter has already been set for Oracle keystore use, so it should not be set again.
-
Open software keystore
SQL> ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER = CDB$ROOT; SQL> SHOW con_name; --Open all the PDBs. SQL> ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ALL OPEN; SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET TDE_CONFIGURATION="KEYSTORE_CONFIGURATION=FILE" scope=both; SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "software_keystore_passphrase" CONTAINER=all; SQL> show pdbs -
Backup software keystore
SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT BACKUP KEYSTORE USING 'backuptag' IDENTIFIED BY "software_keystore_passphrase"; -
Set Hardware Keystore Type.
Set the wallet type to HSM|FILE
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET TDE_CONFIGURATION="KEYSTORE_CONFIGURATION=HSM|FILE" scope=both; -
Migrate from the software keystore to Key Management Vault.
SQL> ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER = CDB$ROOT; SQL> SHOW con_name; --Open all the PDBs. SQL> ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ALL OPEN; SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET ENCRYPTION KEY IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" MIGRATE USING "software_keystore_passphrase" WITH BACKUP; -
Bounce the database
SQL> shutdown immediate; SQL> startup; -
Show wallet and keys
SQL> SELECT CON_ID,WRL_TYPE,STATUS FROM V$ENCRYPTION_WALLET; SQL> SELECT KEY_ID,KEY_USE FROM V$ENCRYPTION_KEYS;
Non-multitenant
The following procedure applies when the target database is non-multitenant, and you are already using a software wallet with TDE encryption.
It is assumed the WALLET_ROOT parameter has already been set for Oracle keystore use, so it should not be set again.
-
Open software keystore
SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "software_keystore_passphrase"; -
Backup software keystore
SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT BACKUP KEYSTORE USING 'backuptag' IDENTIFIED BY "software_keystore_passphrase"; -
Set Hardware Keystore Type
Set the wallet type to HSM|FILE.
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET TDE_CONFIGURATION="KEYSTORE_CONFIGURATION=HSM|FILE" scope=both;
-
Migrate from the software keystore to Key Management Vault.
SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET ENCRYPTION KEY IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" MIGRATE USING "software_keystore_passphrase" WITH BACKUP;
Configuring Auto-login for the Key Management Vault Keystore
To enable Auto-Login with PDB, you need to enable Auto-Login in the container database only. Once you enable Auto-Login in CDB, it would automatically work for PDB. To configure Auto-Login in CDB, follow the below steps:
Connect to the database as sysdba.
% sqlplus / as sysdba-
Close the hardware keystore if it is opened.
SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE CLOSE IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" CONTAINER = ALL; -
Set parameters for software keystore
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET WALLET_ROOT="/opt/oracle/admin/CDB1/wallet" scope=spfile; SQL> shutdown immediate; SQL> startup; SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET TDE_CONFIGURATION="KEYSTORE_CONFIGURATION=FILE" SCOPE=both; SQL> shutdown immediate; SQL> startup; -
Create and open the software keystore
SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT CREATE KEYSTORE IDENTIFIED BY "<software_keystore_password>"; SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "<software_keystore_password>"; -
Add the config file as secret for a client HSM_PASSWORD
Add the secret to the software keystore. This secret is the config file and the client is HSM_PASSWORD. HSM_PASSWORD is an Oracle-defined client name that represents the HSM password as a secret in the software keystore.
SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT ADD SECRET 'file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf' FOR CLIENT 'HSM_PASSWORD' IDENTIFIED BY "<software_keystore_password>" WITH BACKUP USING "<backup_identifier>"; -
Create Auto-login keystore
SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT CREATE AUTO_LOGIN KEYSTORE FROM KEYSTORE IDENTIFIED BY "<software_keystore_password>"; -
Set parameters for software to hardware keystore configuration.
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET TDE_CONFIGURATION="KEYSTORE_CONFIGURATION=HSM|FILE" SCOPE=both; SQL> shutdown immediate; SQL> startup; SQL> SELECT CON_ID,WRL_TYPE,STATUS FROM V$ENCRYPTION_WALLET;
Now when database is started, hardware keystore will be automatically opened.
Rotation of the TDE Key
As with the other key operations, rekey is also initiated in Oracle server. The Oracle server deactivates the existing key and creates a new master key. The encryption key is then wrapped using the new master key. Note that the older key is deactivated but not destroyed.
Make sure that the hardware wallet is open and then run the following command, note the use of FORCE flag.
-
Connect to the database as sysdba.
% sqlplus / as sysdba -
Rotate the key.
-- Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEY FORCE KEYSTORE IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" CONTAINER = ALL; keystore altered. -- Non-Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEY FORCE KEYSTORE IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf"; keystore altered.
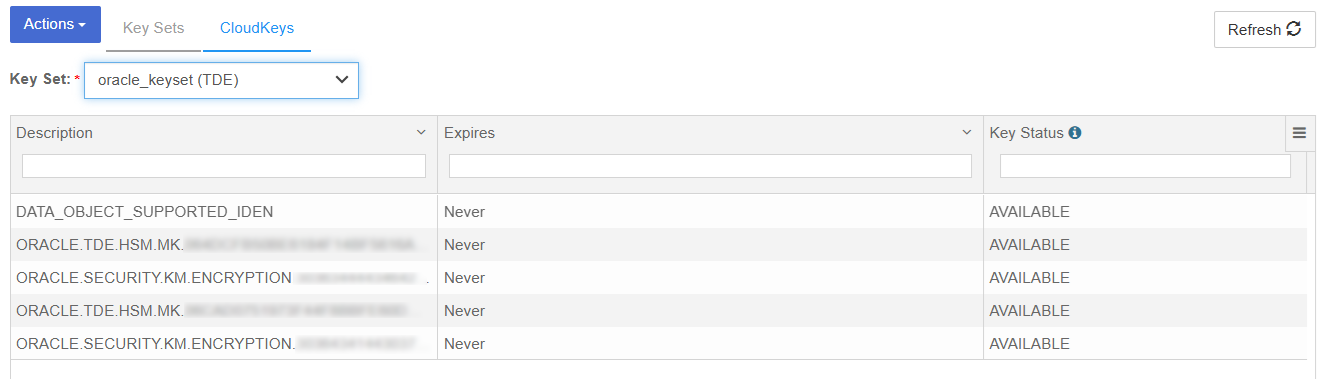
Check the rotation of the keys in the Key Management Vault WebGUI.
You can check rotation of the keys by using the Key Management Vault webGui. You should see the new keys that have been created in the UI.
In the Cryptographic Security Platform Key Management Vault Database Vault webGUI:
-
Navigate to Cloudkeys.
-
Select the CloudKeys tab.
-
For the Key Set, select the TDE keyset created by the TDE setup scripts.
-
You should see the new keys that have been created by the key rotation.
Disable or enable the Database Connector
Disable the Database Connector
-
Log in to the Key Management Vault Database Vault.
-
Select CLOUDKEYS in the top bar.
-
Select the Key Sets tab.
-
Select the desired Key Set and proceed to Database Connectors.
-
Choose the appropriate Database connector and access its settings.
-
Under Actions, locate the option to Disable Connector.
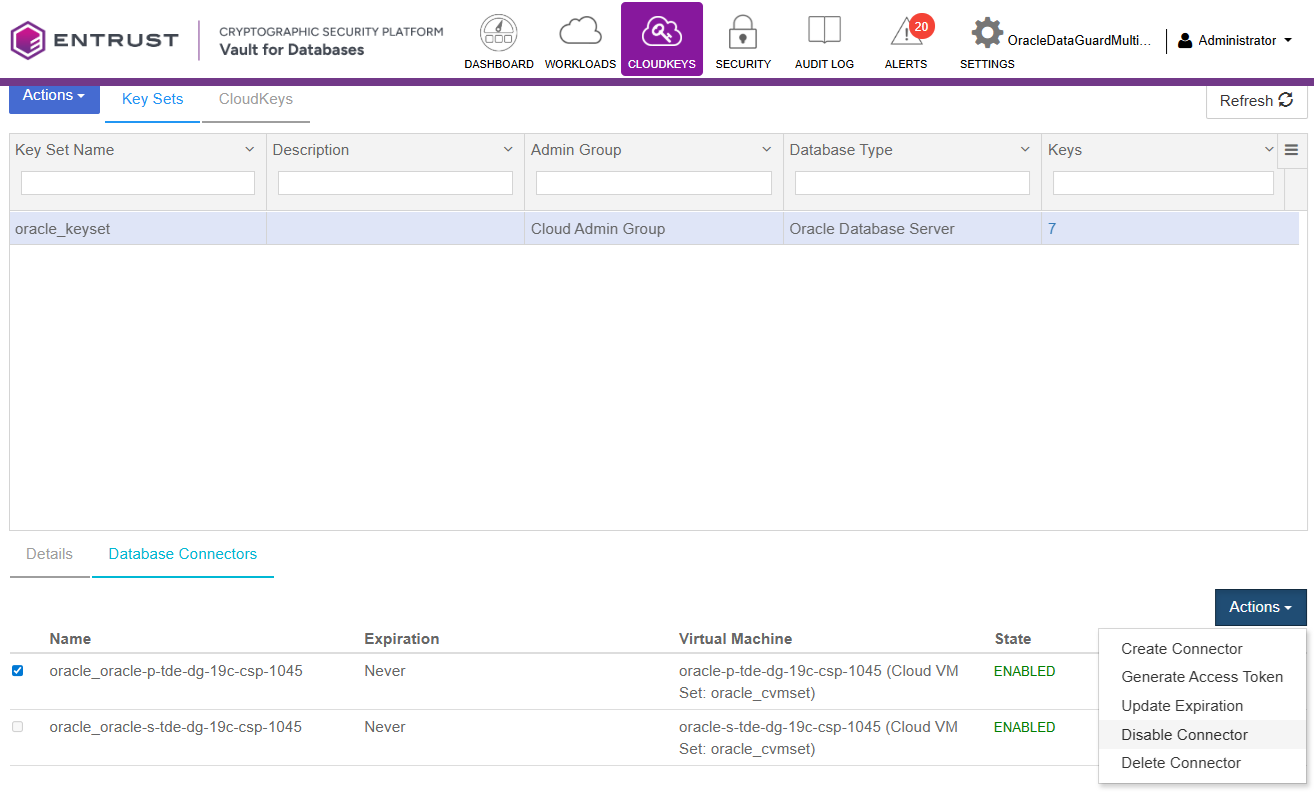
-
Select Disable.
-
Confirm that the state is DISABLED.
-
Return to the Oracle Server and login to SQL as
sysdba. -
When you run the commands to verify the tables, you will notice that it shows the wallet is not open:
ERROR at line 1: ORA-28365: wallet is not open -
Confirm the wallet is closed with the following command:
SQL> select CON_ID,WRL_TYPE,STATUS from V$ENCRYPTION_WALLET; CON_ID WRL_TYPE STATUS ---------- -------------------- ------------------------------ 1 HSM CLOSED 2 HSM CLOSED 3 HSM CLOSED 4 HSM CLOSED
Enable the Database Connector
-
Log in to the Key Management Vault Database Vault.
-
Select CLOUDKEYS in the top bar.
-
Select the Key Sets tab.
-
Select the desired Key Set and proceed to Database Connectors.
-
Choose the appropriate Database connector and access its settings.
-
Under Actions, locate the option to Enable Connector.
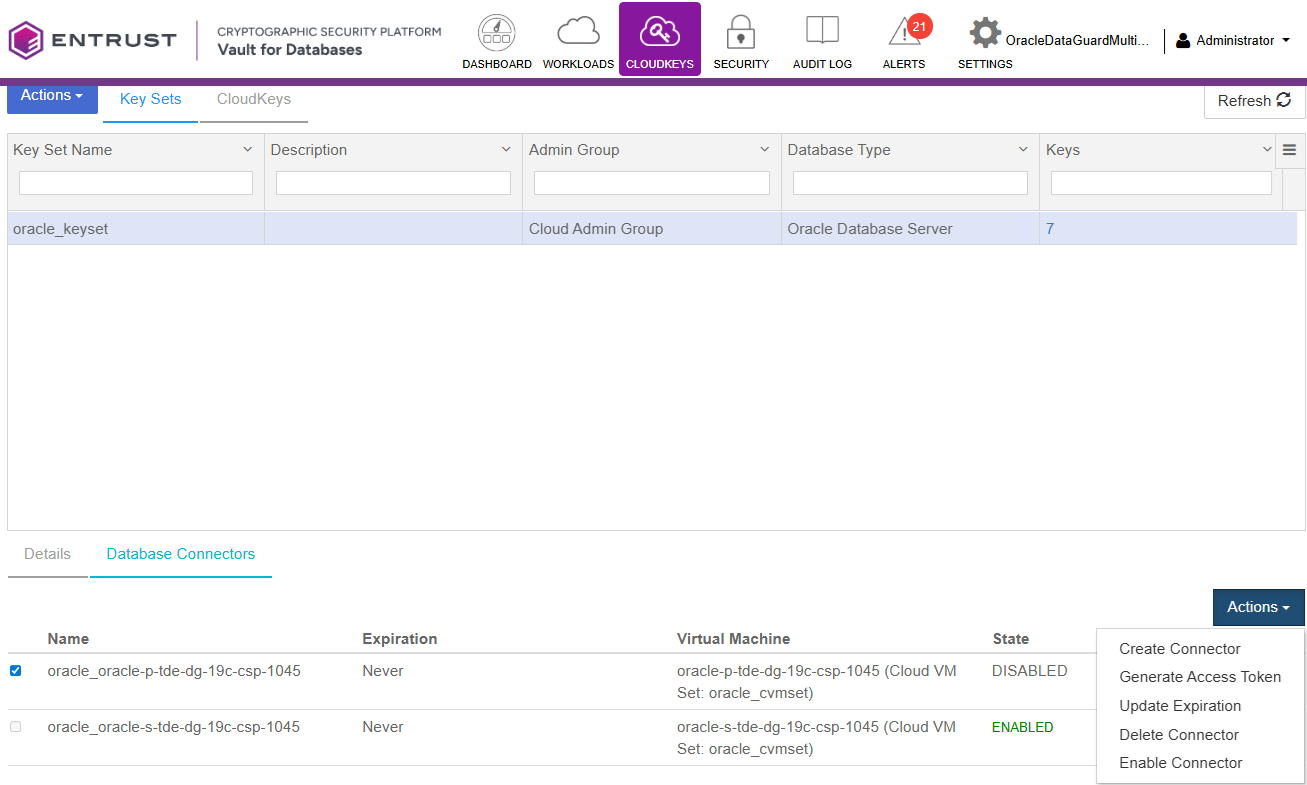
-
Open the keystore:
Return to the Oracle Server and login as
sysdbaand run the following SQL command:SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" CONTAINER=ALL; SQL> select CON_ID,WRL_TYPE,STATUS from V$ENCRYPTION_WALLET; CON_ID WRL_TYPE STATUS ---------- -------------------- ------------------------------ 1 HSM OPEN 2 HSM OPEN 3 HSM OPEN 4 HSM OPEN
Check that you can see the encrypted table content in plaintext
You should be able to do queries on the encrypted tables and see the table content in plaintext.
SQL> select * from employee;
ID NAME SALARY
---------- ------------------------------------------ ----------
1 JOHN LENON 100000
2 MARTINA HINGIS 200000
3 R ATTENBOROUGH 350000Setup of standby node for Data Guard
Now that TDE is working on the primary server and the Oracle environment is setup with Data Guard for disaster recovery, we have to make the keys accessible to the standby VM/s as well. In our examples we created a table with encrypted data and also we encrypted a column in one table. The standby server can not see the encrypted data because TDE is not properly set on the standby yet. You have to ensure the standby server is connected to the same KeySet on the Key Management Vault as well.
Entrust Cryptographic Security Platform Key Management Vault client setup on standby Oracle VM/s
These steps already took place when we first copy the TDE Scripts and run the setup script on the standby server. So you can skip if this already has been performed.
-
Copy the bundle and config file to Oracle server node which will act as standby server.
-
Create a directory and extract the bundle.
-
Copy the modified entrust.conf from the primary Oracle server node and overwrite the config file from the bundle.
-
Setup the client.
Run the setup.sh. You must run this script as the root user or using sudo. Run the setup.sh using bash like this:
sudo ./setup.sh other entrust.confNote that, here the value of node parameter is other.
Oracle standby server setup
The standby server needs to have the TDE wallet configured to be able to see the encrypted data that has been replicating to the standby. If you attempt to see the encrypted data on the standby server, you will see that it is not visible.
-
Connect to the database as sysdba.
% sqlplus / as sysdba -
Attempt to see the data in the
employeetable.SQL> select * from employee; * ERROR at line 1: ORA-00942: table or view does not existLet’s address the issue by configuring the standby server so the encrypted data is visible.
-
Shutdown the database
Start by shutting down the database.
SQL> shutdown immediate; Database closed. Database dismounted. ORACLE instance shut down. -
Set WALLET ROOT
If the
walletdirectory doesn’t exist yet, create it as theoracleuser.% mkdir -p $ORACLE_BASE/admin/$ORACLE_SID/wallet/tdeThen set the
WALLET_ROOTinside SQL.SQL> startup; ORACLE instance started. Total System Global Area 2147481656 bytes Fixed Size 8898616 bytes Variable Size 486539264 bytes Database Buffers 1644167168 bytes Redo Buffers 7876608 bytes Database mounted. Database opened. SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET WALLET_ROOT="$ORACLE_BASE/admin/$ORACLE_SID/wallet" scope=spfile; System altered. SQL> shutdown immediate; -
Set Hardware Keystore Type
Set the wallet type to HSM
SQL> startup; SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET TDE_CONFIGURATION="KEYSTORE_CONFIGURATION=HSM" scope=both; System altered. SQL> shutdown immediate; -
Open the HSM keystore, that is, the keystore backed by Key Management Vault.
SQL> startup mount; -- Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" CONTAINER = ALL; Keystore Altered. -- Non-Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf"; Keystore Altered. -
Restart applying of redo log
SQL> ALTER DATABASE RECOVER MANAGED STANDBY DATABASE USING CURRENT LOGFILE DISCONNECT; Database Altered. -
Show keystore state
SQL> select CON_ID,WRL_TYPE,STATUS from V$ENCRYPTION_WALLET; CON_ID WRL_TYPE STATUS ---------- -------------------- ------------------------------ 0 HSM OPEN_UNKNOWN_MASTER_KEY_STATUSNote that Dataguard mandates that the
DB_UNIQUE_NAMEfor primary and standby servers should be different. Oracle derives application name (CKA_APPLICATION) fromDB_UNIQUE_NAME, so the application name on standby is different. The keys created by primary are marked with primary’s application name. This is why thev$encryption_keysview is an empty list. In the coming release we will add a work around for this issue, but for now best way to verify is to open the database on standby and access the encrypted data. -
Show managed recovery process
SQL> SELECT PROCESS, STATUS, THREAD#, SEQUENCE# FROM V$MANAGED_STANDBY; PROCESS STATUS THREAD# SEQUENCE# --------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ARCH CONNECTED 0 0 DGRD ALLOCATED 0 0 . . . ARCH CONNECTED 0 0 ARCH CONNECTED 0 0 MRP0 APPLYING_LOG 1 24 -
Check the data in the tables in the standby.
You should be able to see the encrypted data in the tables in the standby now. Let’s give it a try. Let’s look at the employee table created earlier. It is encrypted.
SQL> SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE; * ERROR at line 1: ORA-01219: database or pluggable database not open: queries allowed on fixed tables or views onlyNotice that the database is not open. On the standby the database is usually not open. To see the data, you will have to stop redo log, open the database in read only mode and restart the redo log. Then you can see the data.
-
Stop the redo log.
SQL> ALTER DATABASE RECOVER MANAGED STANDBY DATABASE CANCEL; Database altered. -
Open the database in read only mode.
SQL> ALTER DATABASE OPEN READ ONLY; Database altered. -
Restart the redo log.
SQL> ALTER DATABASE RECOVER MANAGED STANDBY DATABASE USING CURRENT LOGFILE DISCONNECT; Database altered. -
Now you should be able to see the data in the employee encrypted table.
SQL> SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE; ID NAME SALARY ---------- ------------------------------------------ ---------- 1 JOHN LENON 100000 2 MARTINA HINGIS 200000 3 R ATTENBOROUGH 350000This shows that Data Guard is working with the encrypted data.
Primary key rotation with Data Guard active
If the master key has to rotated while there is an active data guard managed standby, then the admin has to first stop the redo log apply on standby.
-
Connect to the database as sysdba.
Do this on the primary and standby.
% sqlplus / as sysdba -
Stop the redo log apply on standby
SQL> ALTER DATABASE RECOVER MANAGED STANDBY DATABASE CANCEL; Database altered. -
Rotate the Key on Primary.
This is the same process as done earlier. As with the other key operations, rekey is also initiated in Oracle server. The Oracle server deactivates the existing key and creates a new master key. The encryption key is then wrapped using the new master key. Note that the older key is deactivated but not destroyed.
Make sure that the hardware wallet is open and then run the following command, note the use of FORCE flag.
-- Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEY FORCE KEYSTORE IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" CONTAINER = ALL; keystore altered. -- Non-Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEY FORCE KEYSTORE IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf"; keystore altered. -
Restart the redo log apply on the standby.
Once the master key is rotated on primary, the admin should restart the redo log apply on the standby.
SQL> ALTER DATABASE RECOVER MANAGED STANDBY DATABASE USING CURRENT LOGFILE DISCONNECT; Database altered.When the key is rotated on the primary, the Managed Recovery Process (MRP) on the standby does not get the key immediately. After restarting the redo log, check the status of MRP using following statement:
SQL> SELECT PROCESS, STATUS, THREAD#, SEQUENCE# FROM V$MANAGED_STANDBY; PROCESS STATUS THREAD# SEQUENCE# --------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ARCH CONNECTED 0 0 DGRD ALLOCATED 0 0 DGRD ALLOCATED 0 0 . . . RFS IDLE 1 26 MRP0 APPLYING_LOG 1 26 RFS IDLE 0 0If the MRP has not started applying log, then wait for couple of seconds and then try to restart it again.
Configuring Auto-login for the Key Management Vault Keystore on standby.
Auto login can be enabled on standby server using following steps:
-
Connect to the database as sysdba.
% sqlplus / as sysdba -
Stop the Redo log apply and close the hardware keystore, on standby
SQL> ALTER DATABASE RECOVER MANAGED STANDBY DATABASE CANCEL; -- Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE CLOSE IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" CONTAINER = ALL; -- Non-Multitenant SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE CLOSE IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf"; -
Set parameters for software keystore
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET TDE_CONFIGURATION="KEYSTORE_CONFIGURATION=FILE" SCOPE=BOTH; SQL> SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE; SQL> STARTUP MOUNT; SQL> ALTER DATABASE OPEN READ ONLY; -
Create and open the software keystore
SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT CREATE KEYSTORE IDENTIFIED BY "<software_keystore_password>"; SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "<software_keystore_password>"; -
Add the config file as secret for a client HSM_PASSWORD
Add the secret to the software keystore. This secret is the config file and the client is HSM_PASSWORD. HSM_PASSWORD is an Oracle-defined client name that represents the HSM password as a secret in the software keystore.
SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT ADD SECRET 'file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf' FOR CLIENT 'HSM_PASSWORD' IDENTIFIED BY "<software_keystore_password>" WITH BACKUP USING "<backup_identifier>"; -
Create Auto-login keystore
SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT CREATE AUTO_LOGIN KEYSTORE FROM KEYSTORE IDENTIFIED BY "<software_keystore_password>"; -
Set parameters for software to hardware keystore configuration
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET TDE_CONFIGURATION="KEYSTORE_CONFIGURATION=HSM|FILE" SCOPE=BOTH; SQL> SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE; SQL> STARTUP MOUNT; SQL> SELECT CON_ID,WRL_TYPE,STATUS FROM V$ENCRYPTION_WALLET;Now when database is started, hardware keystore will be automatically opened.
-
Restart the redo log apply on the standby
SQL> ALTER DATABASE RECOVER MANAGED STANDBY DATABASE USING CURRENT LOGFILE DISCONNECT; -
Show the database state
SQL> SELECT name, open_mode, database_role FROM v$database; NAME OPEN_MODE DATABASE_ROLE ---- --------- -------------- CDB1 MOUNTED PHYSICAL STANDBY
Reverse Migration from Key Management Vault to software wallet
Before you start reverse migration, disable Auto login wallet if setup.
-
Connect to the database as sysdba.
% sqlplus / as sysdba -
Set WALLET ROOT
Make sure that the directory exists before running the SQL command:
SQL> alter system set WALLET_ROOT="${ORACLE_BASE}/admin/${ORACLE_SID}/wallet" scope=spfile; -
Bounce the database
SQL> shutdown immediate; SQL> startup; -
Set
TDE_CONFIGURATIONSQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET TDE_CONFIGURATION="KEYSTORE_CONFIGURATION=FILE"; -
Create Software wallet
SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT CREATE KEYSTORE IDENTIFIED BY "software_keystore_passphrase"; -
Ensure that the HSM Keystore, that is the keystore backed by Key Management Vault, is open.
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET TDE_CONFIGURATION = "KEYSTORE_CONFIGURATION=HSM"; SQL> ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=CDB$ROOT; SQL> ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ALL OPEN; SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" container=all; SQL> select CON_ID,WRL_TYPE,STATUS from V$ENCRYPTION_WALLET; -
Reverse Migrate to Software Keystore
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET TDE_CONFIGURATION = "KEYSTORE_CONFIGURATION=FILE|HSM" SCOPE=BOTH SID='*'; SQL> ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET ENCRYPTION KEY IDENTIFIED BY "software_keystore_passphrase" REVERSE MIGRATE USING "file:/opt/oracle/entrust/oracle.conf" WITH BACKUP; -
Show wallet and keys
SQL> SELECT CON_ID,WRL_TYPE,STATUS FROM V$ENCRYPTION_WALLET; SQL> SELECT KEY_ID,KEY_USE FROM V$ENCRYPTION_KEYS;
Backup or restore
When using Key Management Vault, when doing a backup and restore, make sure Entrust policy agent is setup on the restore node as well. Before recovering the restored database, the HSM keystore has to be opened. Refer the Oracle documentation for details of RMAN based backup /restore.