TSOP v8.0.0 Administrator Guide
Introduction
The Entrust nShield Time Stamp Server (TSS) provides secure and auditable time signing for electronic business transactions and documents. The TSS serves as a reliable source for time signing, and enables you to:
-
Provide authoritative proof of when an event has occurred
-
Ensure that time-stamps are secure, authentic, and auditable.
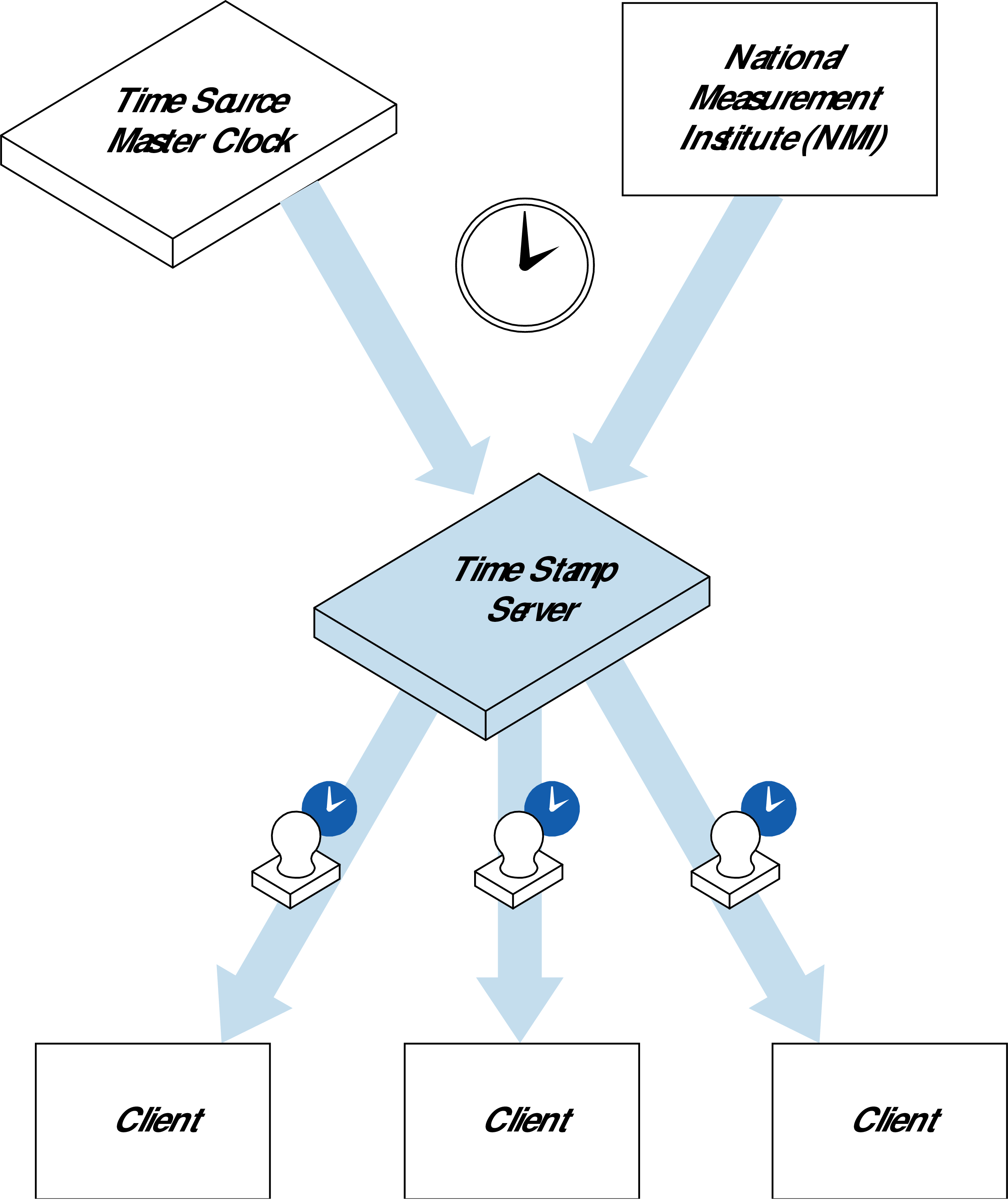
TSS trust model
The Universal Co-ordinated Time (UTC) is the world standard for time. The TSS obtains UTC from one of the following sources:
-
Time Source Master Clock (TSMC): TSMC serves as an intermediate node for the acquisition and distribution of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). or more information, see the Time Source Master Clock Administrator Guide.
-
National Measurement Institute (NMI): An NMI acts as a source of UTC for its country. An NMI supplies time to a hierarchy of lower clocks such as the TSS, which make UTC available to applications.
The TSMC or the NTP server (from the NMI) calibrates the TSS at regularly scheduled intervals, depending on the accuracy required. During this process, all transactions are digitally signed and logged. All communication is by means of an authenticated, secure network connection.
After calibrating and auditing the TSS, the TSMC or the NTP server issue a signed Time Attribute Certificate (TAC) for:
-
Authorizing the operation of the TSS
-
Certifying the calibration and traceability of the TSS. The TSS can then issue time-stamps for any Extended Public Key Infrastructure (PKIX) compliant time sign request.
A time-stamp includes:
-
Details of the actual time it was issued.
-
A hash of the digital information being time signed.
-
A time certification or calibration pointer. The certification provides the necessary information to confirm that the time signing is accurate, valid, and traceable back to an official time authority.
The time-stamps issued by TSS conform to the IETF Time-Stamp and Time-Stamp Token protocols.